{{item.title}}
{{item.text}}

{{item.text}}
PwC Switzerland’s Trust in AI services pave the way for robust models and responsible AI practices
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of both our personal and professional lives. Yet, it often raises concerns and reservations. What if your voice-activated application records all your conversations? Or if your automated driving assistant makes decisions that seem unpredictable? To avoid such scenarios, it is crucial to develop, operate, and maintain responsible AI systems.
At PwC Switzerland, we are dedicated to unlocking the vast potential of AI while ensuring its responsible and ethical use. Our Trust in AI services are designed to instil confidence in your AI initiatives by rigorously validating and refining models to deliver optimal output. With a strong commitment to responsible AI practices, we help organisations navigate the complex landscape of artificial intelligence, promoting transparency, fairness, and accountability in the deployment of AI solutions. Trust in AI starts with PwC Switzerland.
Participate in our survey to gain a deeper understanding of your current status, compare yourself to your peers and shape the future of responsible AI.
AI offers enormous opportunities, yet integrating AI into an organisation also entails risks. We are committed to supporting our clients in effectively managing these challenges and building a responsible AI framework.
Yan BorboënPartner, Leader Digital Assurance & Trust, PwC SwitzerlandAs with any powerful tool, there are inherent risks in adopting AI. Companies must balance speed and confidence when implementing AI, ensuring a risk-based approach to gain competitive advantages and maintain stakeholder trust. Effective risk management is vital to fully reaping the benefits of this transformative technology.
Discussions about the ethical aspects of AI, such as the potential for deepfakes, bias, and intellectual property infringement, are crucial. And the fears about the technology’s impact on employment and its potential to replace aspects of human intelligence must be taken seriously too.
Building trust in the use of AI entails a full understanding of the risks, and a clear approach to addressing them – as well as stakeholder concerns – in an effective and compelling way. Only by emphasising human involvement, robustness, fairness, security, privacy and governance, businesses can skilfully navigate the AI landscape and realise its full potential.
Read more about the risks associated with AI in our blog How is your organisation dealing with AI?
Dealing with AI-generated information requires caution, curiosity, and a discerning eye. Effective risk management is the cornerstone of success. To prosper with AI and secure a competitive advantage, an organisation must establish a robust risk management framework that not only protects against potential pitfalls, but also unlocks opportunities.
Such a risk-based approach to AI also sets the stage for a positive relationship with regulators, consumers, and other stakeholders.
Fostering trust in an AI-driven world requires a holistic view and understanding of potential risks at all stages of the AI lifecycle as well as a strategic approach to proactively mitigate these risks.
Morgan BadoudDirector Digital Assurance & Trust, PwC SwitzerlandAs we’ve been building AI solutions since 2016, we’ve identified key areas of risk and how best to deal with them:
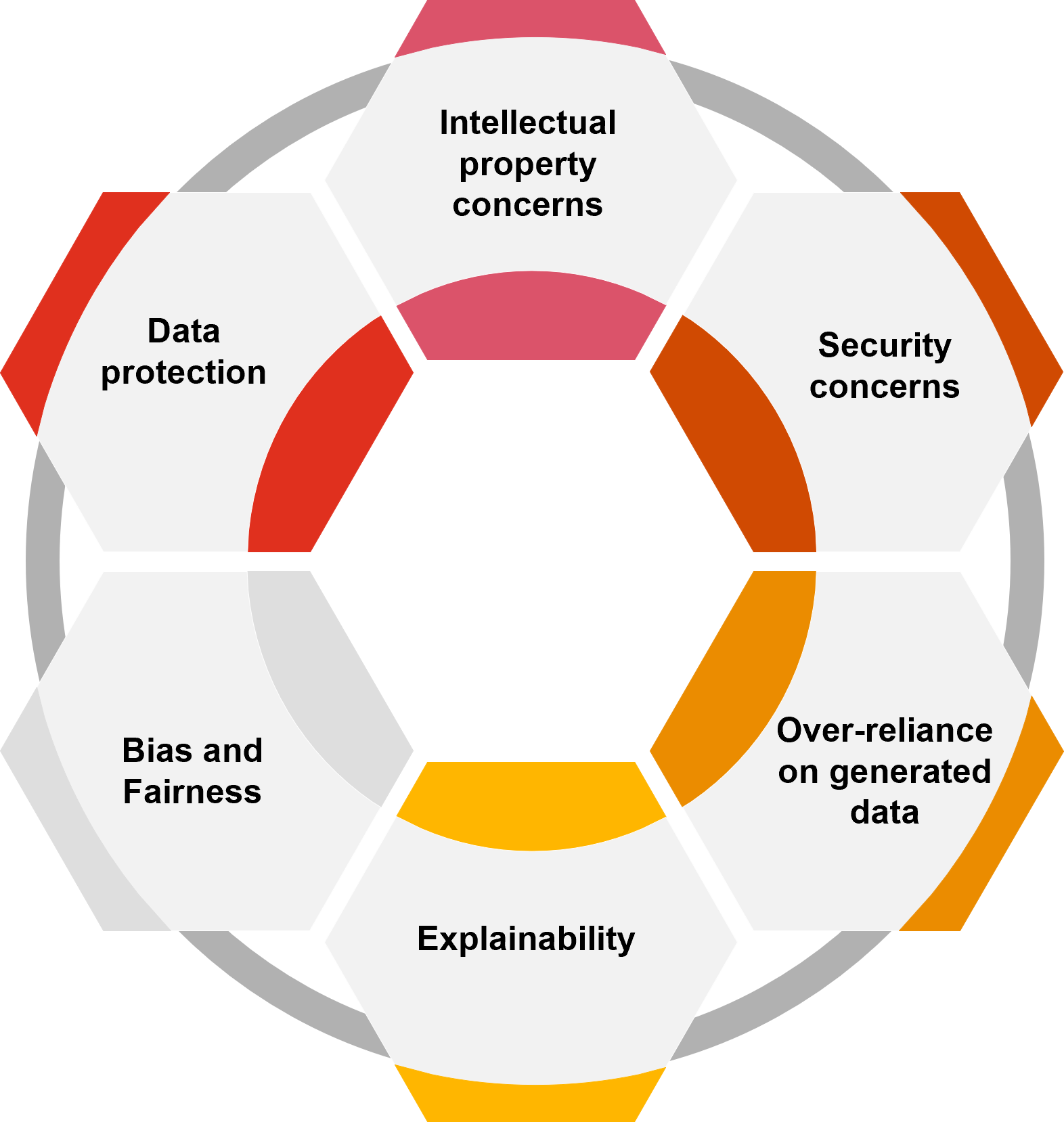
Data protection
Key data protection considerations include conducting comprehensive risk assessments, ensuring transparency, obtaining informed consent, vigilantly monitoring for bias, implementing data retention policies, and regularly reviewing and updating these policies to ensure compliance and security.
Security concerns
Addressing security concerns in AI involves assessing potential risks, implementing robust security controls, training employees on security best practices, keeping software updated with regular patches, and using third-party validation to strengthen security measures.
Over-reliance on generated data
To mitigate the risk of over-reliance on generated data, it’s important to educate stakeholders on the limitations of AI, establish clear guidelines for its use, validate generated data against real-world data sources, and continuously monitor and review the use of generated data in decision-making processes.
Explainability
To address model explainability concerns, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations of the model and its training data. Use interpretable models whenever possible, conduct thorough model evaluations, and stay informed about the latest developments in explainable AI techniques to increase transparency and understanding.
AI models and algorithms create original data by identifying patterns in existing data sets. These models produce outputs that reflect their training inputs but show distinctive variations. Applications are broad and diverse, including image generation, text and speech synthesis, music composition, and more. But they also carry the potential for bias if not properly trained and validated. Despite these challenges, however, AI models will play a growing role in data generation and decision-making across industries and applications.
From hyper-personalised marketing campaigns and improving customer experience, to streamlining business operations, workforce management and supply chain optimisation, to fraud detection and legal issues, AI is transforming industries.
However Generative AI is not merely a technological advancement, it is a catalyst reshaping the very foundation of how businesses operate. Given its vast possibilities, Generative AI is not limited to certain business functions but impacts the entire value chain of an organization.
Considering the multitude and broadness of potential fields of application, it is not surprising that organizations are struggling to navigate themselves through the possibilities Generative AI has to offer. In addition, the majority of organizations are seeing the impact AI has and have understood the need for a comprehensive AI strategy and transformation roadmap. However, given common challenges, such as limited IT and innovation budgets, they rather choose to start small with selected use cases to prove the value Generative AI has before deciding about larger investments. Therefore, actively steering the portfolio to maximize ROI is critical to the success of Generative AI in organizations. Some of the key questions and challenges we see currently in the market are the following:
However Generative AI is not merely a technological advancement, it is a catalyst reshaping the very foundation of how businesses operate. Given its vast possibilities, Generative AI is not limited to certain business functions but impacts the entire value chain of an organization.
While identifying risks related to AI and mitigating them, responsible AI emphasizes ethical design, transparency, fairness, and accountability in artificial intelligence systems. It aims to ensure AI respects human rights, avoids biases, maintains privacy, and operates ethically, fostering trust and benefiting society while minimizing potential harms.
Take a deep dive into the ethics of data and AI use, and embed them in your organisational values. Stay ahead of the curve in policy and regulation by anticipating and understanding critical policy and regulatory developments, enabling alignment with compliance processes for responsible AI implementation.
In terms of governance, it’s essential to establish monitoring mechanisms that encompass all three lines of defence within your organisation. In compliance, prioritise adherence to regulations, internal organisational policies, and industry standards. Within risk management, extend your traditional risk detection and mitigation practices to effectively address the unique risks and potential harms associated with AI technologies.
When implementing AI, it’s important to ensure interpretability and transparency; AI models should make transparent decisions for clear understanding. Sustainability should be a priority, with the aim of reducing environmental impact. The AI systems must be robust and reliable, while also addressing potential biases and ensuring fairness. Cybersecurity is crucial to protect from threats, and privacy concerns must be addressed by data protection measures. Finally, safety is key, with AI systems designed and tested to prevent physical harm and ensure safe use.
Clearly define the specific problem and assess whether AI/ML is the appropriate solution. Adhere to industry best practices and standards to ensure consistency and quality. Continuously evaluate model performance and make iterative enhancements to improve metrics. Implement ongoing monitoring to identify changes in performance and potential risks.
The AI landscape is full of open frontiers, offering vast opportunities, but also significant challenges. A cautious approach to AI is crucial, ensuring that ethics and human input remain central. Building AI systems on a solid ethical foundation is essential, considering their impact on all users.
Our multi-disciplinary teams, with extensive experience in designing and implementing AI solutions, will guide you through the critical steps and provide ongoing support as you embark on a successful AI transformation.
Our approach to AI is based on four pillars: enablement, suitability assessment, third-party assurance, and education.
Trust in transformation – To remain competitive in the digital age, companies need a strategic approach to AI that focuses on security and transparency. Many AI projects fail early, often due to insufficient digital trust across the AI lifecycle, including data protection, bias in model training, and uncertainties in AI performance and robustness. Success depends on defining and implementing the right organisational and technological strategies in services and products. We guide you through the necessary steps to realise the full potential of AI and accompany you on your journey to a successful Responsible AI.
PwC is speeding up its commitment to AI technology, forging industry partnerships, focusing on training, and enhancing its client services — initiatives that have already positioned us as a forerunner in the field of AI. Our approach to implementing AI in businesses is based on building trust and achieving results. These principles form the backbone of our lab-based innovations and our tangible AI solutions.
In addition to our direct involvement with businesses, we actively participate in discussions and bodies that are shaping the ethical standards and practices of responsible AI.
{{item.text}}

{{item.text}}
Talk to our AI experts to find out how PwC can help you use AI responsibly and harness its potential in an ethical and conscientious way.
https://pages.pwc.ch/core-contact-page?form_id=7014L000000IIaSQAW&embed=true&lang=en
Mark Meuldijk
Angelo Mathis